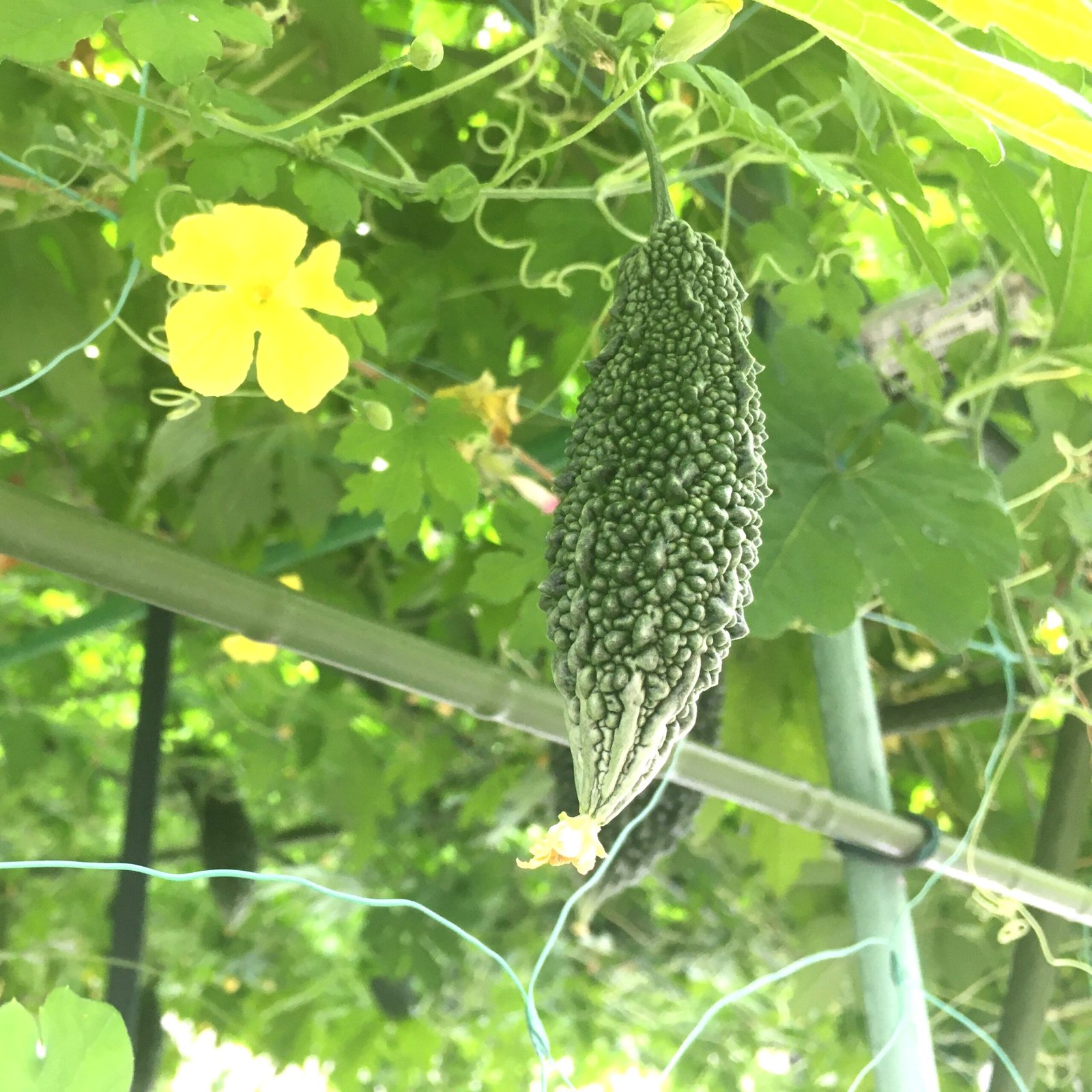
Bittergourd Long, commonly known as Karela in India, is a popular vegetable appreciated for its distinctive bitter flavor and numerous health benefits. Below are the comprehensive product details for Bittergourd Long Karela Vegetable Seeds:
Botanical Name: Momordica charantia
Common Names: Bittergourd, Bitter Melon, Karela
Fruit Characteristics:
Shape: Elongated and cylindrical with a warty exterior.
Color: Dark green skin when immature, turning yellowish upon full maturity.
Size: Typically 15 to 20 cm in length.
Weight: Approximately 120 to 130 grams per fruit.
Flavor: Distinctively bitter taste, which can be reduced by soaking in salted water before cooking.
Culinary Uses: Commonly used in Indian, Chinese, and Southeast Asian cuisines; suitable for stir-fries, curries, and pickles.
Plant Characteristics:
Growth Habit: Vigorous climbing vine with tendrils; requires support for optimal growth.
Leaves: Deeply lobed, providing good foliage cover.
Flowers: Yellow, unisexual flowers; male flowers typically appear first, followed by female flowers.
Pollination: Primarily insect-pollinated; presence of pollinators like bees enhances fruit set.
Maturity Period: Harvestable within 55 to 60 days after sowing.
Yield: High-yielding variety with multiple harvests over the growing season.
Cultivation Details:
Climate: Thrives in warm, humid climates; sensitive to frost.
Soil: Prefers well-drained, fertile loamy soil with a pH of 6.0 to 7.0.
Sowing Depth: 1 to 1.5 cm deep.
Spacing: 60 cm between plants; 1.5 to 2 meters between rows.
Sunlight: Requires full sun exposure for optimal growth.
Watering: Regular watering to maintain consistent soil moisture; avoid waterlogging.
Fertilization: Benefits from organic compost and balanced NPK fertilizers; side-dressing with nitrogen enhances growth.
Planting and Harvesting Seasons in India:
North India:
Summer Crop: Sow from February to March.
Monsoon Crop: Sow from June to July.
South India:
Summer Crop: Sow from January to February.
Monsoon Crop: Sow from June to July.
Harvesting: Begins approximately 55 to 60 days after sowing; frequent harvesting encourages continuous fruiting.
Pest and Disease Management:
Common Pests: Aphids, fruit flies, and red pumpkin beetles.
Common Diseases: Powdery mildew, downy mildew, and mosaic virus.
Management Strategies: Implement crop rotation, use resistant varieties, apply organic or chemical controls as needed, and maintain proper field sanitation.
Special Features:
Nutritional Value: Rich in vitamins C and A, iron, and antioxidants; known for potential blood sugar-lowering properties.
Health Benefits: Traditionally used in herbal medicine for its anti-inflammatory, and digestive properties.





















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.